
- #SYSTEMRESCUECD INSTALLER FOR WINDOWS FOR FREE#
- #SYSTEMRESCUECD INSTALLER FOR WINDOWS HOW TO#
- #SYSTEMRESCUECD INSTALLER FOR WINDOWS INSTALL#
- #SYSTEMRESCUECD INSTALLER FOR WINDOWS CODE#
- #SYSTEMRESCUECD INSTALLER FOR WINDOWS TRIAL#
It is only possible to have up to four primary partitions on a hard disk, so, depending on the Linux partitions you decide to create, it is possible that you will need to create an extended partition containing logical partitions. You can download the ISO file from the SystemRescueCd Web site. SystemRescueCD is a good LiveCD to use for running GParted, but any LiveCD/DVD which includes GParted will suffice. Also, I have found on some occasions that installation of some Linux distributions fails if using the partitioning tool integrated in the Linux installer, but is successful if the partitions were created beforehand. GParted has more functionality and enables better control over the partitioning process than a partitioning tool incorporated in the Linux distribution’s installer. I prefer to use GParted to create the partitions before running the Linux distribution’s installer, rather than using a partitioning tool integrated into the Linux installer itself. Stage 2: Create the new partitions for Linuxīoot a LiveCD or LiveDVD which has the partition editor GParted on it, and run GParted to create and format partitions for Linux (for example /, /boot, /home and swap) in the free space you created in Stage 1 above.
#SYSTEMRESCUECD INSTALLER FOR WINDOWS TRIAL#
Basically you need to download a tool such as PerfectDisk (it has a free trial period) that will defragment the Windows partition and move the MFT in the process. Step C: If you cannot shrink the Windows partition to the size you want by using Windows’ Disk Management, then you need to move the MFT (see Working Around Windows Vista’s “Shrink Volume” Inadequacy Problems). However, if you are satisfied with the resulting size of the Windows partition then you can skip Step C below and proceed directly to Stage 2. The problem with this method is that Windows will only shrink the partition until it reaches the MFT (Master File Table), which means there may be free space in the Windows partition that you would have wanted to use in a Linux partition but cannot.
#SYSTEMRESCUECD INSTALLER FOR WINDOWS FOR FREE#
Step B: Use Windows’ Disk Management to shrink the partition (see Resize a Partition for Free in Windows 7 or Vista). Step A: Use the Windows defragmenter or a third-party defragmenter to defragment the Windows partition.
Stage 1: Reduce the size of the existing Windows partitionĭo not use the partition managers Parted, GParted or KDE Partition Manager to reduce the size of the existing Windows partition, or you will damage your Windows installation.
#SYSTEMRESCUECD INSTALLER FOR WINDOWS INSTALL#
If you already have Windows installed, the procedure to prepare the PC and install Linux is divided into the following three main stages. So, to reiterate, the method described below avoids two potential major problems: 1) it avoids the possibility of making a Windows factory restore partition unusable 2) it avoids the possibility of Windows applications overwriting some of the GRUB 2 code.
#SYSTEMRESCUECD INSTALLER FOR WINDOWS CODE#
The method described below does not install any GRUB 2 code in the MBR, and thus it will avoid this problem. See the blog article Windows applications making GRUB 2 unbootable for details. Note also that some Windows applications can make a PC using GRUB 2 unbootable if GRUB 2 is installed in the MBR. If the contents of the original MBR are overwritten - even if it is only by using the Bootrec.exe tool on a standard Windows Vista/7 Installation DVD - then the manufacturer’s code will no longer be in the MBR and so it will no longer be possible to boot the hidden factory restore partition by pressing the key(s) specified by the manufacturer.
The reason why this is the best method is because it does not alter the contents of the MBR (Master Boot Record), which, in addition to the Windows bootloader, may contain code created by the manufacturer to boot the hidden factory restore partition instead of the Windows Vista/7 partition if it detects that you pressed a defined key or keys while the PC is booting.
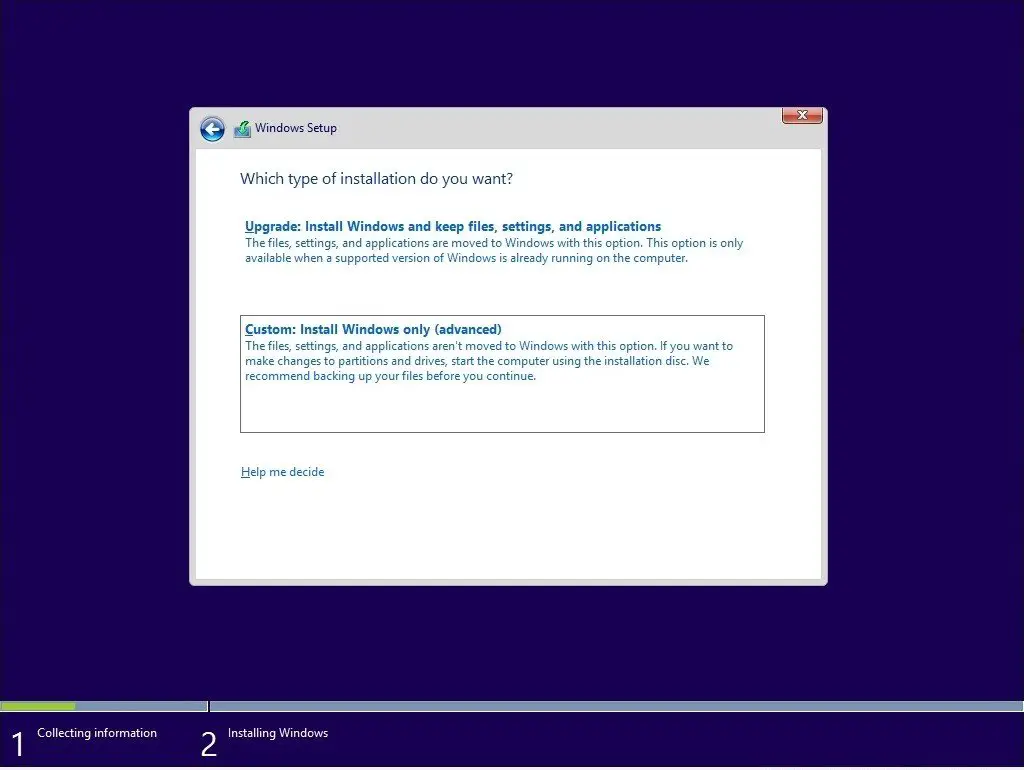
If you already have Windows Vista or Windows 7 installed in a single partition, then the method described below is the best way of ensuring that your Windows installation will still be bootable even if the Linux installation or GRUB bootloader become damaged in future.įurthermore, if your PC has a hidden factory restore partition for Windows, the method described below is the best way of ensuring that you will still be able to recover Windows in future using that hidden partition.
#SYSTEMRESCUECD INSTALLER FOR WINDOWS HOW TO#
I’m going to explain how to configure your PC in order to dual boot Linux and Windows Vista or Windows 7, assuming Windows is already installed.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
